Pablo Picasso was of the opinion that "a painter should create that which he experiences".
As one goes along in life, there are plenty of experiences that mark one, positively and negatively. As an artist, there are times when you can "digest" an experience fairly quickly and it will show up in your art in a relatively straightforward fashion. Perhaps the most direct way to depict experiences pictorially is plein air painting or drawing. You are filtering through onto paper or canvas your sensory experiences of an area, urban or rural, coastal or upland, whatever.
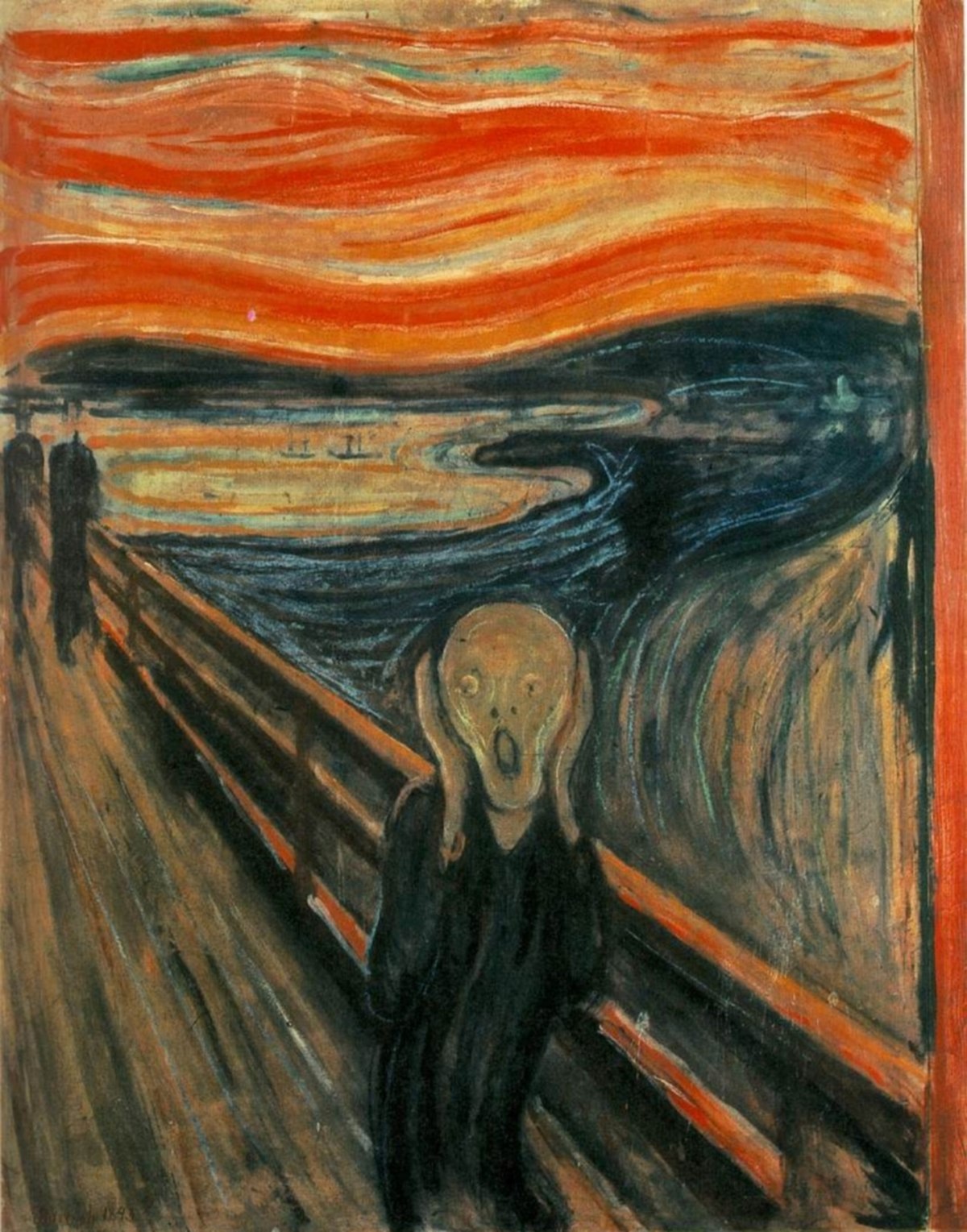
When an artist's life goes through major ups or downs, those experiences are more complex, but sooner or later, they do seem to show up in a serious artist's work. Perhaps one of the most famous examples of art arising from life experiences is The Scream which Edvard Munch painted when he was 30 years old.
The Scream,Edvard Munch, oil, 1893, (Image courtesy of the National Gallery, Oslo, Norway
He had had a very difficult life from childhood. He wrote about his father, "My father was temperamentally nervous and religiously obsessive - to the point of psychoneurosis. From him, I inherited the seeds of madness. The angels of fear, sorrow and death stood by my side since the day I was born." By the time he had moved to Berlin and then to Paris, experimenting with different artistic styles, he was coping with deep anguish and angst. He later said about this painting that, "for several years, I was almost mad. I was stretched to the limit - nature was screaming in my blood. After that, I gave up hope ever of being able to love again."
Picasso spoke very accurately of his art being derived from his experiences. His Blue Period paintings were influenced by the suicide of his friend, Carlos Casagemas. His love affairs with his various mistresses were the source of the amazing work that continued to flow from him during his long and productive life. Borrowed experiences are also sometimes the source of great art. Again, Picasso is a prime example, with Guernica, which was created after the Germans bombed the small town of Guernica during the Spanish Civil War.
Guernica, Pablo Picasso (Image courtesy of the Reina Sofia Museum, Madrid)
Other artists believe in placing "the visible at the service of the invisible", as 19th century Symbolist Odilon Redon said. His inner experiences were channeled into strange pastels and paintings which often had an initial appearance of real subjects, but then then veer into the grotesque and ambiguous.
The Cactus Man 1881, Odilon Redon, Charcoal on paper (Image courtesy of Museum of Modern Art, New York )
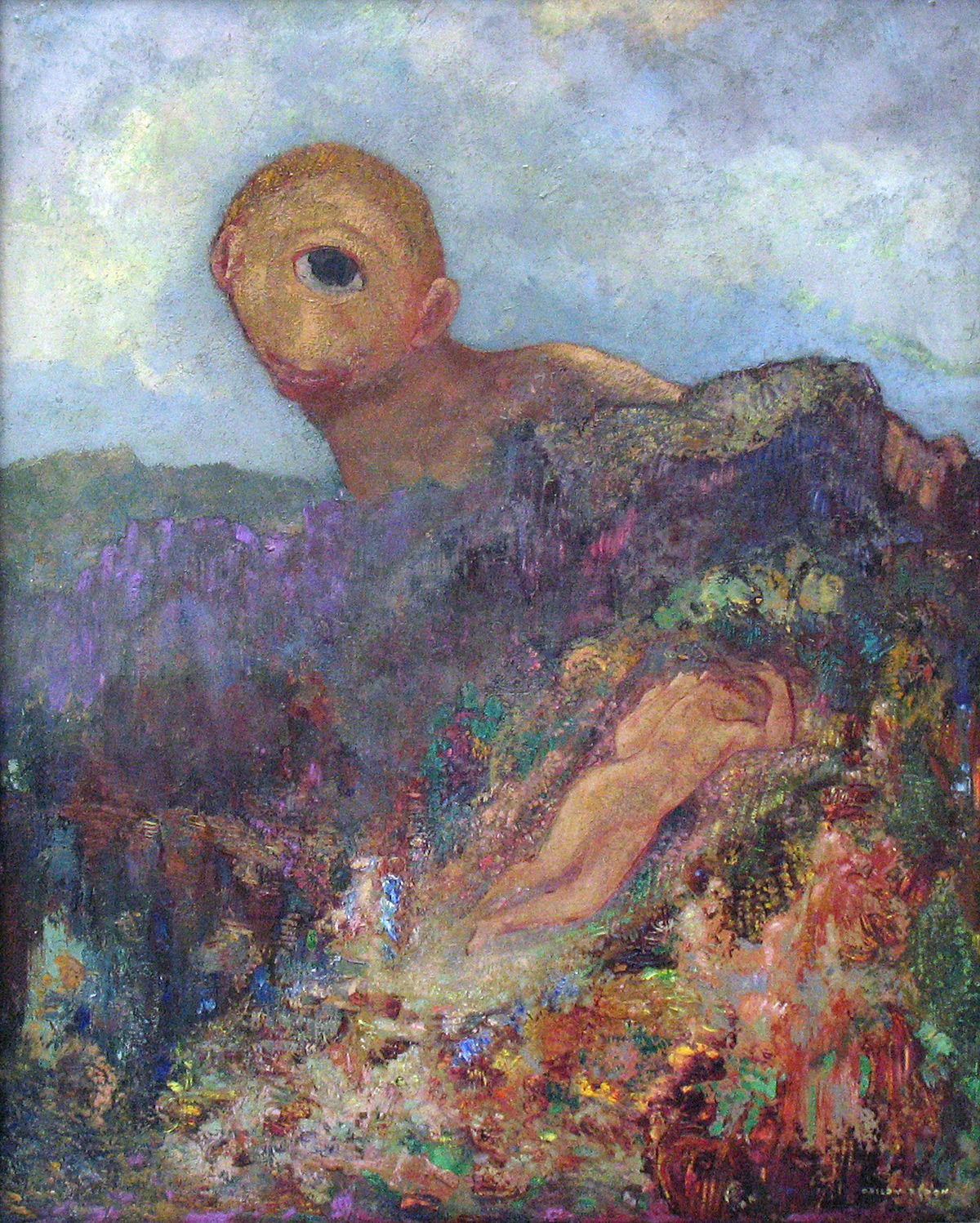
The Cyclops, 1914 by Odilon Redon. Symbolism. mythological painting. Kröller-Müller Museum, Otterlo, Netherlands.
The Cactus Man (1881) is one of Redon's strange drawings. But there is a consistency that runs through his work, for in 1914, he paints The Cyclops . One can only conjecture at the personal experiences that drive these works of art.
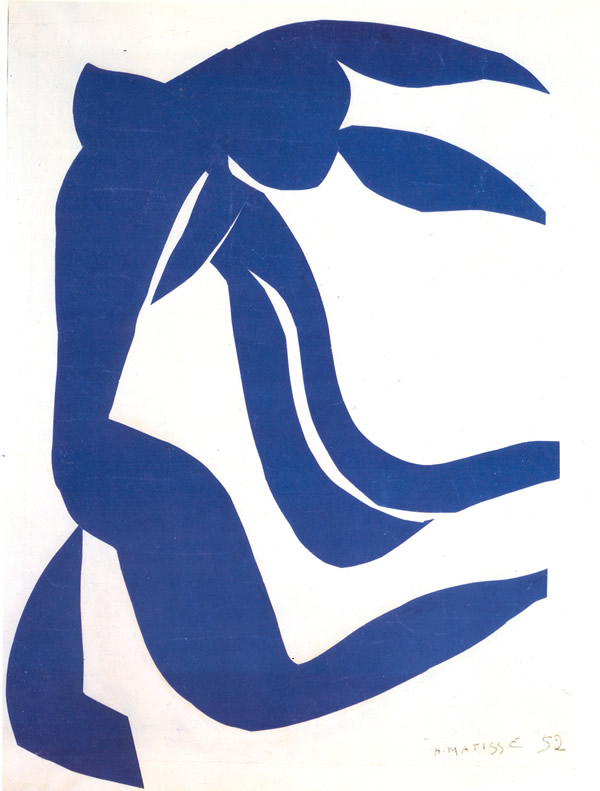
Another type of experience that led to wonderful art is when Henri Matisse was increasingly unwell, towards the end of his life, and was confined to a wheel chair after 1941. So he turned to "painting with scissors" and produced his wonderfully joyous cut outs, his Blue Nudes from 1952 and his limited edition book, Jazz, with its series of colourful cut paper collages, amongst others.
Blue Nude with her Hair in the Wind, 1952, gouache-painted paper cut outs, Henri Matisse (Image courtesy of www,henri-matisse.com)
Today's artists have such a wide array of examples of how artists drew on their personal experiences to inspire their art. It makes a very strong case for each of us to believe in ourselves as artists, to listen to our inner voices and follow their inspiration into creating strongly individual art.